After falling by 1.6% in the first three months of this year, the US economy shrank by 0.9% in the 2nd quarter. For comparison, the growth rate of the world’s largest economy reached 6.9% in annual terms in the 4th quarter of 2021. This is a record figure for the last 40 years. Leading economists surveyed by The Wall Street Journal expected the US economy to show a slight, but still 0.4% growth in the 2nd quarter.
The decline in US GDP in the 2nd quarter is explained by a reduction in private investment in inventories that is due to a decline in retail trade, a drop in real estate investment, and public expenditures. At the same time, the economic shrinking is taking place against the background of a record acceleration of inflation in the country, historically low unemployment, and the hawkish monetary policy of the US Federal Reserve.
The decline in GDP growth over two quarters is traditionally considered to be the beginning of a technical recession. However, the US Department of Commerce puts a broader meaning to this term: a recession includes a significant drop in business activity in most sectors of the economy for several months, unemployment, output and household income.
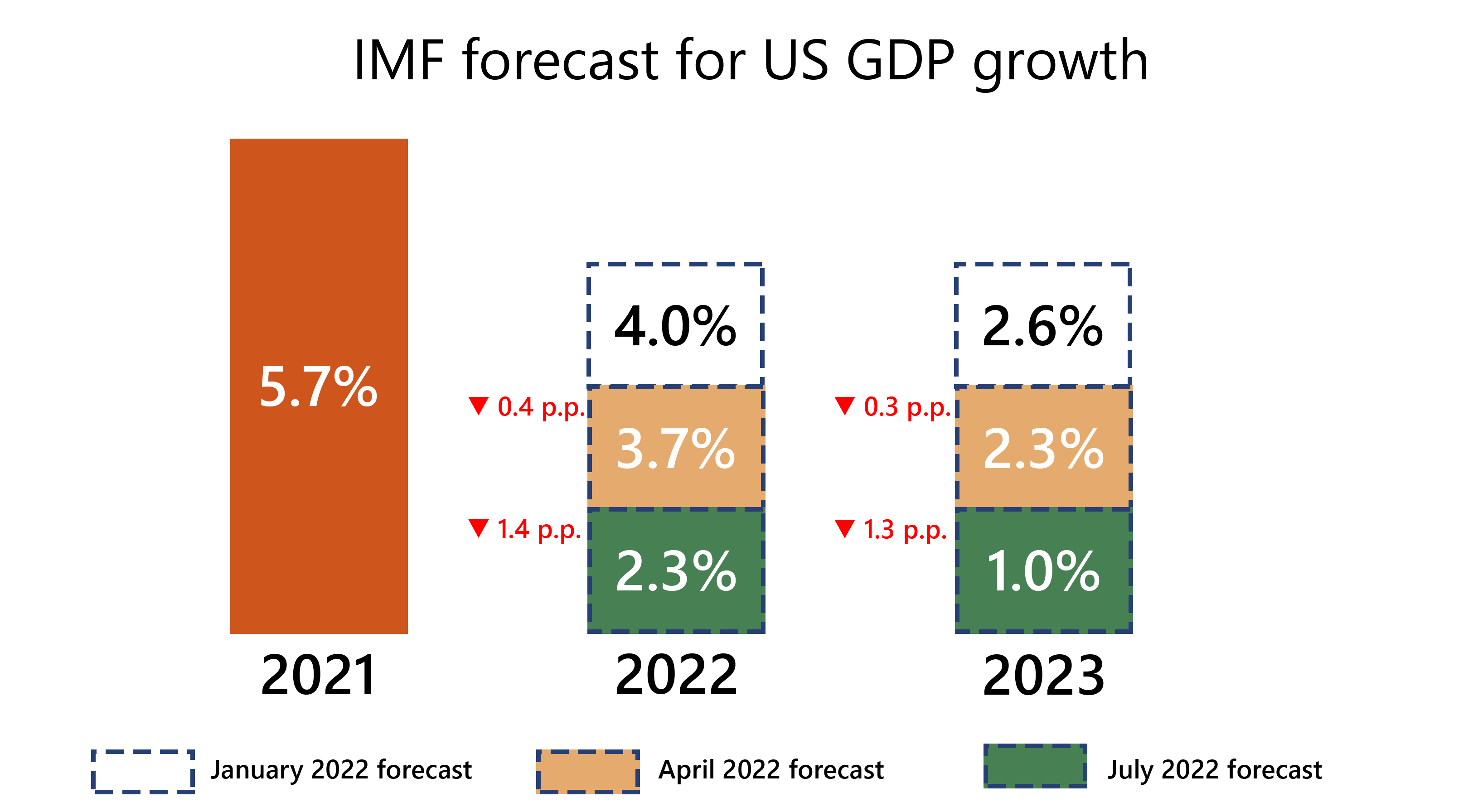
The International Monetary Fund lowered the projected growth rates of US GDP in its updated July report. According to the latest forecasts of the organization, the US economy will shrink by 2.3% this year and 1.0% next year, which is 1.4 and 1.3 percentage points lower than the April review.
 Рафаэль Жансултанов
Рафаэль Жансултанов
